PKI Training - Difference between Cryptography and Encryption!
Cryptography:
The discipline that embodies the principles, means, and methods for providing information security, including confidentiality, data integrity, source authentication, and non-repudiation. Source(s): NIST SP 800-175B Rev. 1 under Cryptography
It is to be noted that Cryptography provides not only encryption but many other services.
Encryption:
- Cryptographic transformation of data (called “plaintext”) into a form (called “ciphertext”) that conceals the data’s original meaning to prevent it from being known or used. If the transformation is reversible, the corresponding reversal process is called “decryption,” which is a transformation that restores encrypted data to its original state. Source(s): NIST SP 800-82 Rev. 2 under Encryption from RFC 4949
- Any procedure used in cryptography to convert plain text into cipher text to prevent anyone but the intended recipient from reading that data. NIST SP 800-101 Rev. 1 under Encryption. NIST SP 800-72 under Encryption
Following are the domains of Cryptography:
- Symmetric Cryptography
- Asymmetric Cryptography
- Hashing Domain (for integrity)
Symmetric Cryptography:
A cryptographic algorithm that uses the same secret key for its operation and, if applicable, for reversing the effects of the operation (e.g., an AES key for encryption and decryption). Source(s): NIST SP 800-77 Rev. 1
Asymmetric Cryptography: The purpose of encryption can also be achieved using the asymmetric Key Cryptography. Additionally, Asymmetric Key Cryptography also provides services of data integrity, source authentication, and non-repudiation.
- Encryption system that uses a public-private key pair for encryption and/or digital signature. Source(s): CNSSI 4009-2015 under public key cryptography (PKC)
- Cryptography that uses two separate keys to exchange data, one to encrypt or digitally sign the data and one for decrypting the data or verifying the digital signature. Also known as public key cryptography. Source(s): NIST SP 800-77 Rev. 1 under Asymmetric Cryptography
Digital Signature: The services of data integrity, Source authentication and non-repudiation are achieved through usage of signing services.
- The result of a cryptographic transformation of data which, when properly implemented, provides the services of: 1. origin authentication, 2. data integrity, and 3. signer non-repudiation. Source(s): NIST SP 800-12 Rev. 1 under Digital Signature from FIPS 140-2
- An asymmetric key operation where the private key is used to digitally sign data and the public key is used to verify the signature. Digital signatures provide authenticity protection, integrity protection, and non-repudiation, but not confidentiality protection. Source(s): NIST SP 800-63-3 under Digital Signature NISTIR 8011 Vol. 3 under Digital Signature from NIST SP 800-63-3
- The result of applying two cryptographic functions (a hash function, followed by a digital signature function; see FIPS 186-3 for details). When the functions are properly implemented, the digital signature provides origin authentication, data integrity protection and signatory non-repudiation. Source(s): NIST SP 800-107 Rev. 1 under Digital signature
As per the FIPS 186-3 (Digital Signature Standard):
Process of Digital Signature:
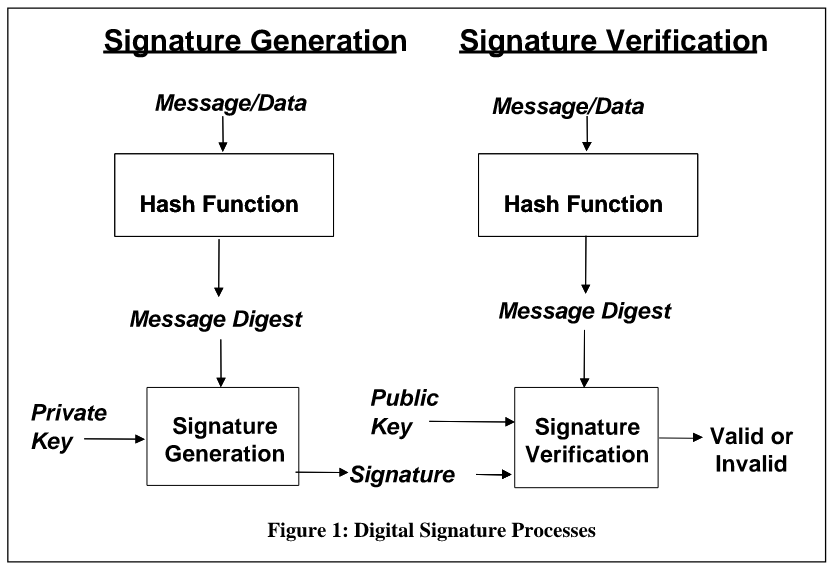 {:width=“80%”}
{:width=“80%”}
Generation of Digital Signature:
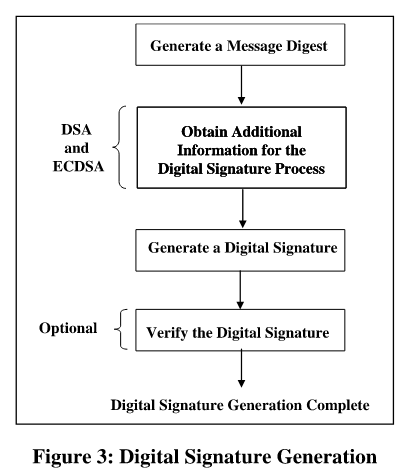 {:width=“80%”}
{:width=“80%”}
Verification of Digital Signature:
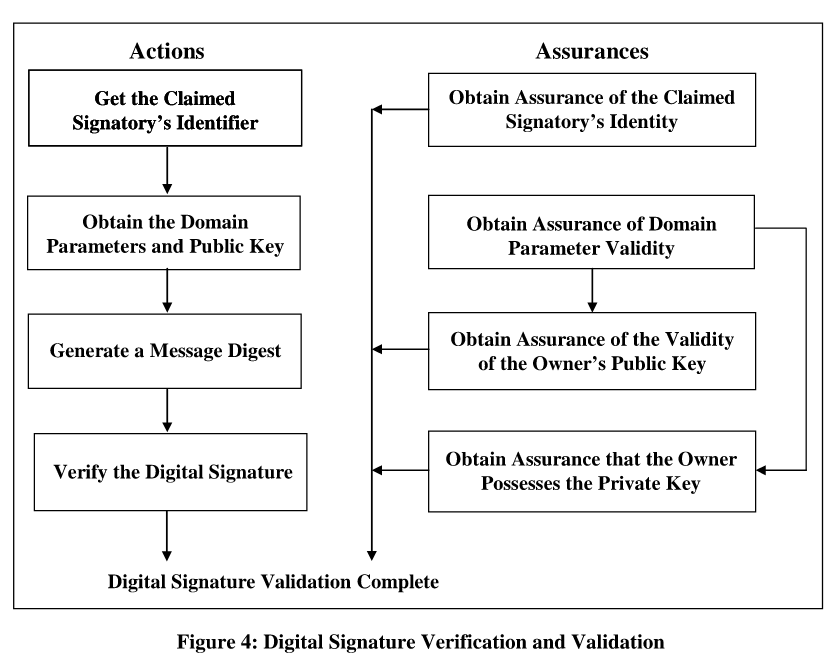 {:width=“80%”}
{:width=“80%”}